Mastering AWS S3: A Comprehensive Guide from Beginner to Pro
Introduction
Amazon Simple Storage Service (AWS S3) is one of the most popular and versatile cloud storage solutions. In this guide, we will take you from understanding the basics of AWS S3 to mastering advanced features like versioning, lifecycle policies, and encryption.
Whether you’re just getting started or looking to fine-tune your knowledge, this blog will cover everything you need to know about S3 buckets, object storage, and best practices.
🌐 What is AWS S3?
AWS S3 is a scalable, secure, and durable object storage service that allows users to store and retrieve any amount of data at any time. It provides flexibility and simplicity, making it ideal for a range of use cases, including:
- Backup and restore
- Big data analytics
- Content storage and delivery
For beginners, AWS S3 provides an easy-to-use GUI that allows you to create and manage storage buckets directly from the AWS Management Console.
🗂️ Key Concepts in AWS S3
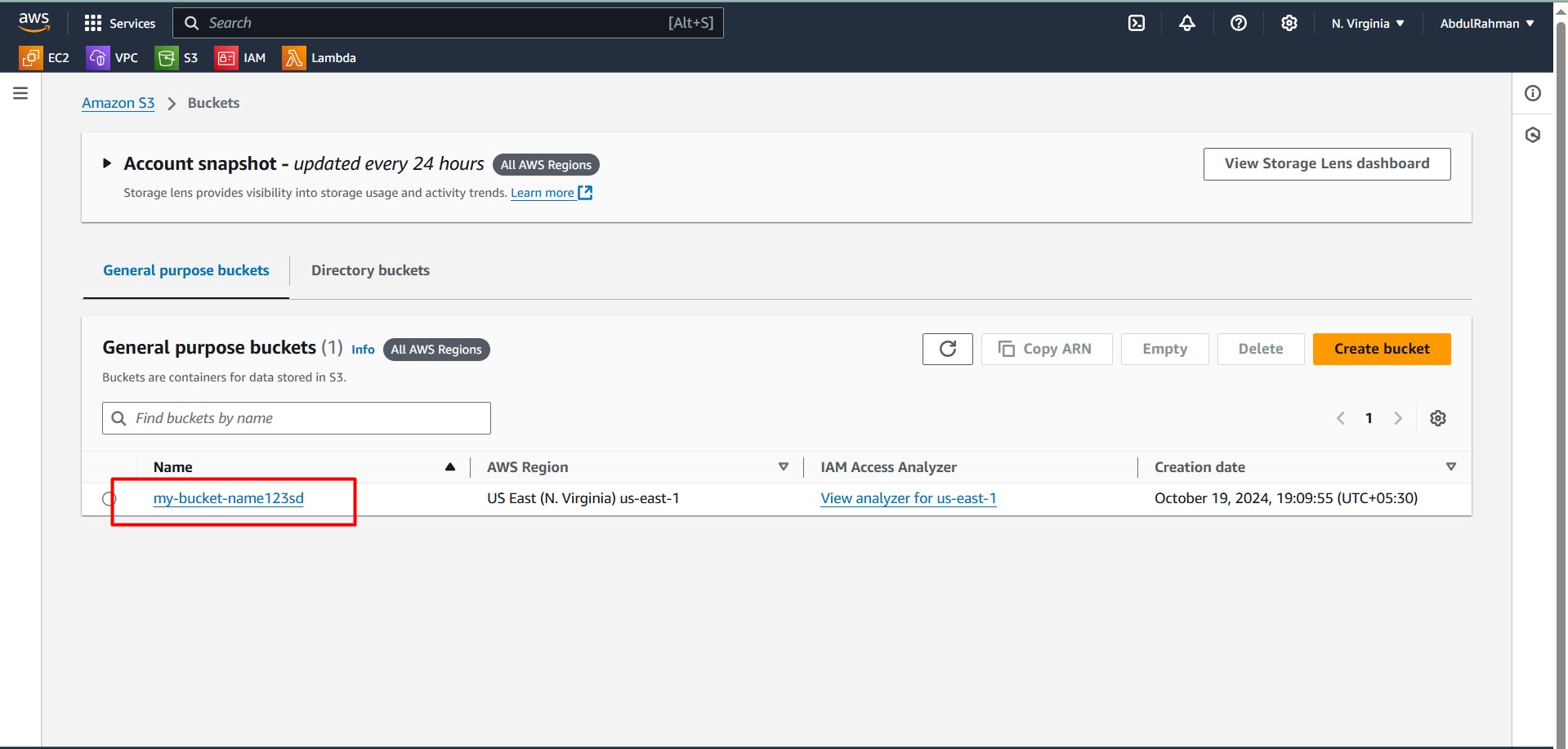
1. Buckets
Buckets are the fundamental containers in S3 that hold your data (objects). Each bucket has a globally unique name and can store an unlimited number of objects.
GUI Steps:
- Go to the S3 Management Console.
- Click on Create bucket.
- Enter a unique bucket name and choose a region.
Example:
aws s3 mb s3://my-bucket-name
2. Objects
An object in S3 consists of the data you want to store and its metadata. Each object is uniquely identified within a bucket by a key (the file name).
GUI:
- Upload objects via Add files in the AWS Console.
Example:
aws s3 cp my-file.txt s3://my-bucket-name/
🔐 S3 Security and Access Control
1. Bucket Policies
Bucket policies define the permissions for accessing the bucket and its objects. You can configure public access or restrict it to specific users.
GUI Steps:
- Open the S3 Console.
- Navigate to Permissions for your bucket.
- Edit the Bucket policy to control access.
Example Policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": "s3:GetObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket-name/*"
}
]
}
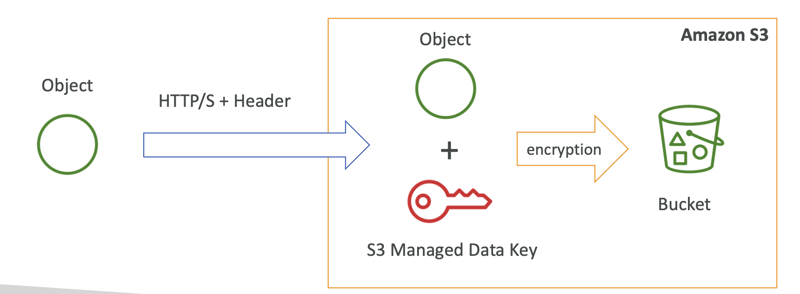
2. Encryption
S3 provides several options for encrypting your data, both at rest and in transit.
- Server-Side Encryption (SSE) with Amazon S3-managed keys (SSE-S3).
- Client-Side Encryption for encrypting data before uploading.
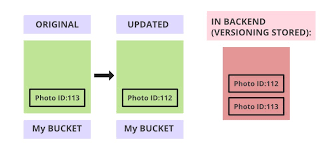
📜 Versioning in AWS S3
S3 versioning allows you to store multiple versions of an object in the same bucket, enabling rollback in case of accidental deletion or overwriting.
GUI Steps to Enable Versioning:
- Open the S3 Management Console.
- Select your bucket.
- Click on Properties and enable Versioning.
Enabling Versioning via CLI:
aws s3api put-bucket-versioning --bucket my-bucket-name --versioning-configuration Status=Enabled
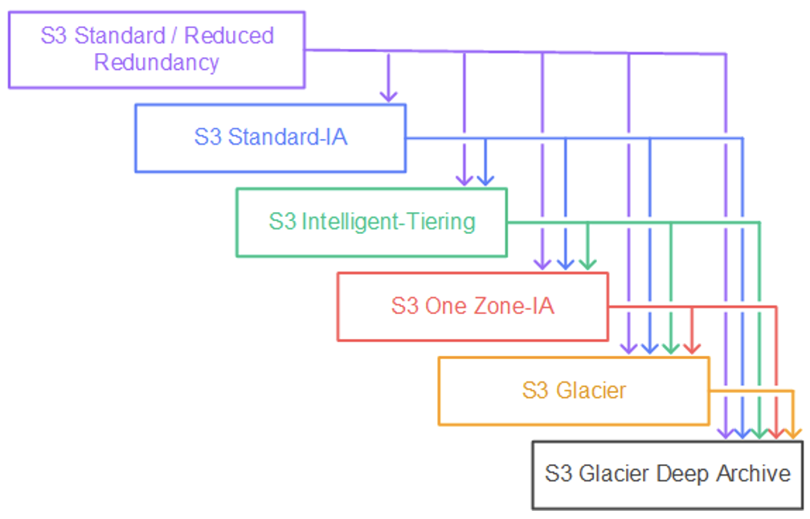
🔄 S3 Lifecycle Policies
Lifecycle policies help manage the lifecycle of your objects by automating transitions between storage classes and expiring outdated objects.
GUI Steps:
- Go to Management tab in the S3 console.
- Click Create lifecycle rule to configure rules for moving or deleting objects based on time.
Example Lifecycle Policy:
{
"Rules": [
{
"ID": "Archive older objects",
"Prefix": "",
"Status": "Enabled",
"Transitions": [
{
"Days": 30,
"StorageClass": "GLACIER"
}
],
"Expiration": {
"Days": 365
}
}
]
}
🔧 Installing AWS CLI (Advanced)
For advanced users, installing the AWS CLI allows you to manage S3 from the command line.
Installation (Windows)
- Download the installer from AWS CLI Installer for Windows.
- Run the installer and follow the prompts.
- Verify installation by typing the following in Command Prompt:
aws --version
🛠️ Advanced Features for Pro Users
1. S3 Object Lock
S3 Object Lock enables you to store objects using a write-once-read-many (WORM) model to help meet regulatory requirements.
2. S3 Replication
You can replicate objects across different regions for redundancy or compliance with S3 Cross-Region Replication (CRR).
Advanced operations like creating buckets or uploading files via CLI:
aws s3 mb s3://my-bucket-name
aws s3 cp my-file.txt s3://my-bucket-name/
🚀 Best Practices for AWS S3
- Enable versioning for critical data.
- Use S3 Intelligent-Tiering to optimize storage costs.
- Set up lifecycle policies to archive infrequently accessed data.
- Regularly audit your security settings using AWS CloudTrail and CloudWatch.
📈 Conclusion
AWS S3 is a robust, versatile storage solution suitable for both beginners and advanced users. Whether you’re managing backups or serving data-intensive applications, mastering S3 will enhance your cloud computing skills.

Leave a comment