PySpark for Data Engineers: Build Scalable Data Pipelines
Introduction
In the era of big data, processing large datasets efficiently is crucial. Apache Spark, an open-source distributed computing system, has become a go-to tool for handling massive data workloads. PySpark is its Python API, making it easier for data engineers and analysts to work with Spark using Python.
In this guide, we will explore PySpark’s architecture, key components, and practical commands to help you get started with big data processing.
🔥 What is PySpark?
PySpark is the Python interface for Apache Spark, allowing users to leverage Spark’s powerful distributed computing capabilities using Python. It is widely used for big data analytics, machine learning, and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes.
Why Learn PySpark?
- 🚀 Handles large datasets efficiently
- ⏳ Faster than traditional frameworks like Pandas for big data
- 🔀 Works seamlessly with distributed computing clusters
- ☁️ Supports cloud platforms like Databricks and Google Cloud
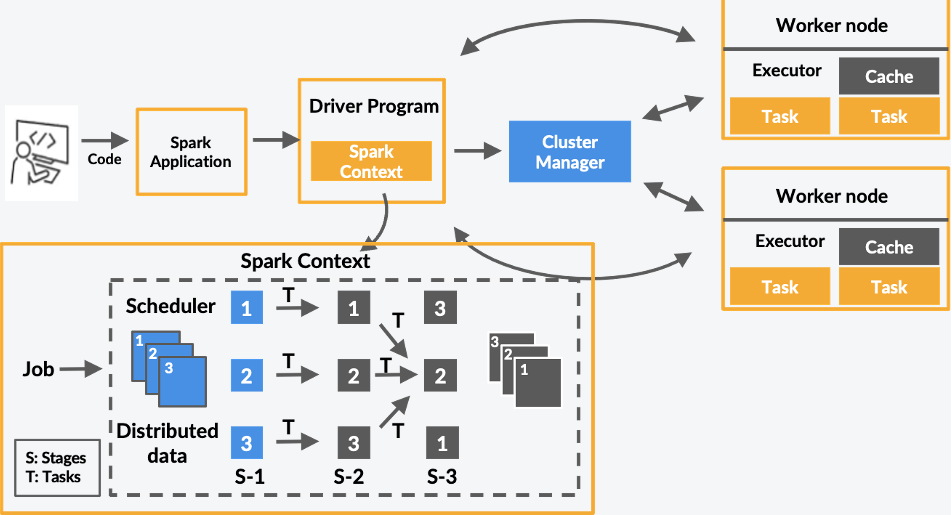
🏗 PySpark Architecture
PySpark follows a distributed computing model, breaking large tasks into smaller ones that run in parallel. Its architecture includes:
1️⃣ Driver Program
- The driver is the main control program that runs the SparkContext.
2️⃣ Cluster Manager
- Allocates resources across a cluster (e.g., YARN, Mesos, Kubernetes, or Standalone mode).
3️⃣ Executors
- Run tasks assigned by the driver and store data in memory or disk.
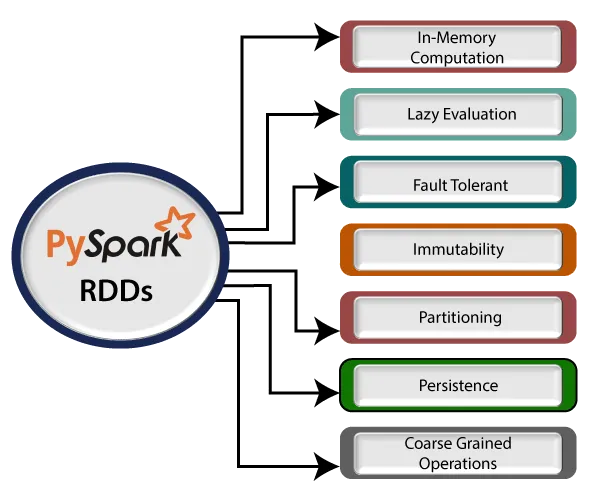
4️⃣ RDDs (Resilient Distributed Datasets)
- The fundamental data structure in Spark, ensuring fault tolerance and parallel processing.
🛠 Setting Up PySpark
You can install PySpark using pip:
pip install pyspark
To start PySpark in an interactive mode:
pyspark
For Jupyter Notebook users:
pip install jupyter findspark
Then, in Python:
import findspark
findspark.init()
import pyspark
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("MyApp").getOrCreate()
print(spark)
📊 PySpark Components
PySpark consists of several key components:
1️⃣ SparkContext
- The entry point to Spark’s core functionality.
from pyspark import SparkContext
sc = SparkContext("local", "MyApp")
print(sc)
2️⃣ SparkSession
- The unified entry point for working with DataFrames and Datasets.
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("MyApp").getOrCreate()
3️⃣ RDDs (Resilient Distributed Datasets)
- Immutable, distributed collections of data.
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(rdd.collect()) # [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
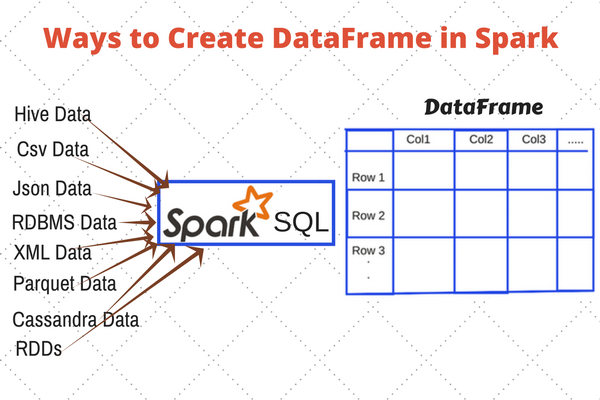
4️⃣ DataFrames
- Similar to Pandas DataFrames but optimized for distributed processing.
data = [("Alice", 25), ("Bob", 30)]
columns = ["Name", "Age"]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, columns)
df.show()
⚡ Essential PySpark Commands
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
df.show() |
Displays the DataFrame |
df.printSchema() |
Prints schema of DataFrame |
df.select("col") |
Selects a specific column |
df.filter(df["col"] > value) |
Filters data |
df.groupBy("col").count() |
Groups data and counts occurrences |
df.orderBy("col") |
Sorts data |
df.withColumn("new_col", df["col"] * 2) |
Adds a new column |
Example:
df.show() # Displays the DataFrame
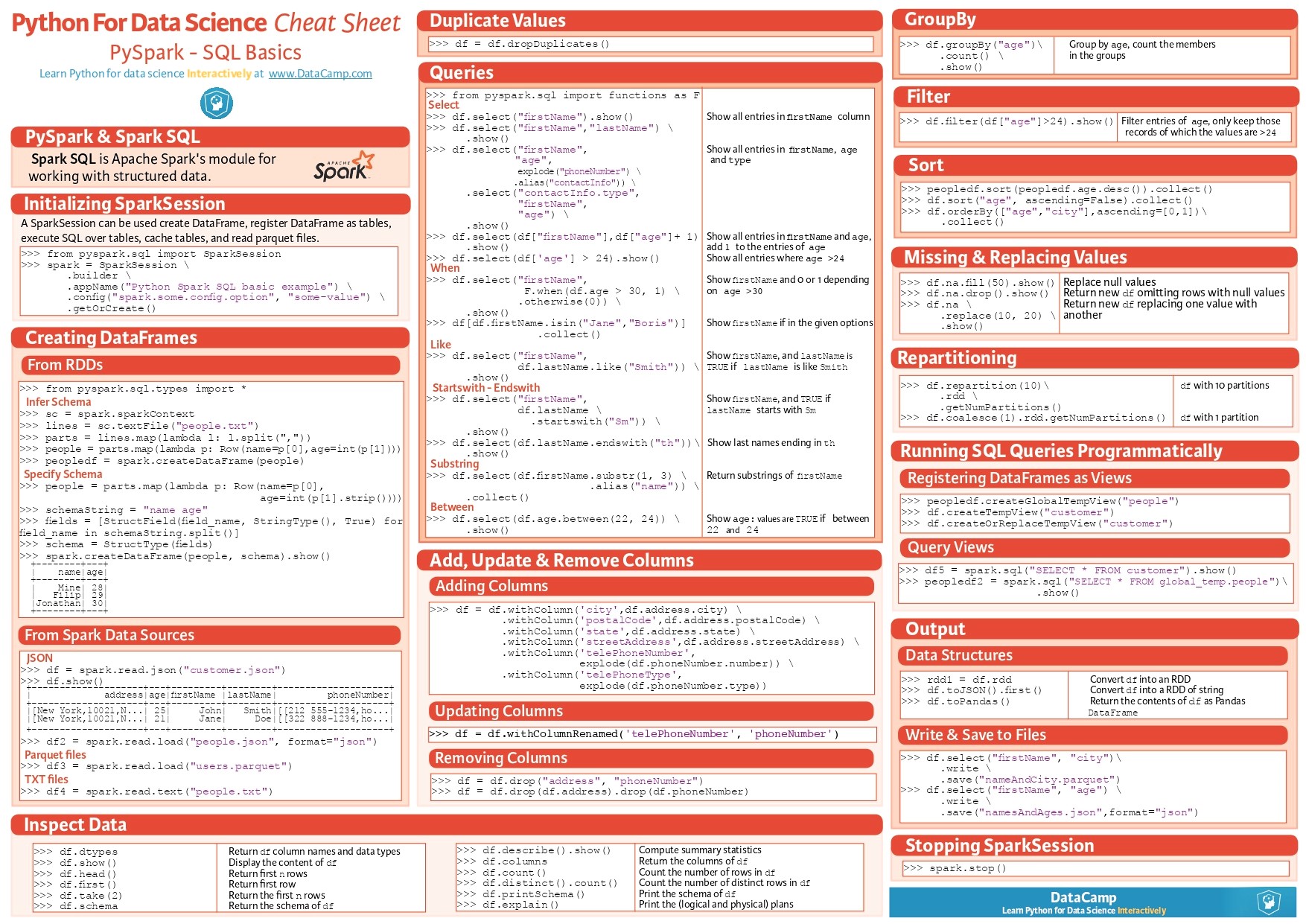
📌 PySpark Cheat Sheet
🎯 Tips to Learn PySpark Faster
- ✅ Start with small datasets before moving to big data.
- ✅ Practice using DataFrames and RDDs in Jupyter Notebook.
- ✅ Explore official documentation and community resources.
- ✅ Work on real-world datasets to solidify concepts.
- ✅ Try cloud-based platforms like Databricks for hands-on experience.
🎯 Conclusion
PySpark is a powerful tool for processing big data at scale. With its support for distributed computing and cloud platforms like Databricks, it is a must-have for any data engineer. This guide covered:
- PySpark architecture & components
- Essential commands & DataFrame operations
Now you’re ready to dive deeper into big data processing with PySpark! 🚀
Happy Pysparking!

Leave a comment