What is Hadoop? A-Z of Hadoop and Big Data
Big Data has transformed the way organizations manage and analyze their data, and Hadoop is at the heart of this transformation. Let’s dive into what Hadoop is, its components, and its role in the Big Data ecosystem.
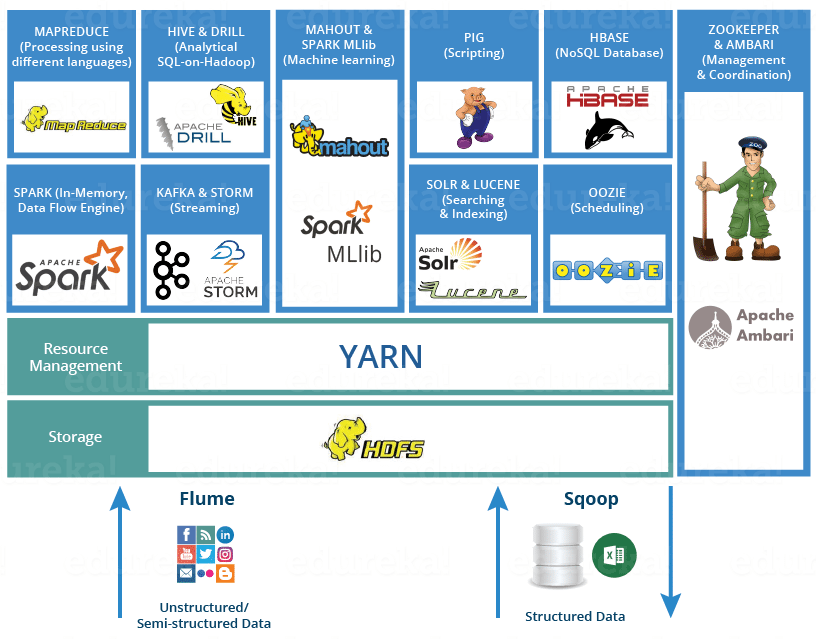
What is Hadoop?
Hadoop is an open-source framework designed to handle vast amounts of data across a distributed network of computers. It allows for the processing of large datasets in a parallel and efficient manner, making it a cornerstone of Big Data technologies.
Key Features:
- Scalability: Hadoop can scale from a single server to thousands of machines.
- Fault Tolerance: Data is automatically replicated across multiple nodes to ensure high availability.
- Cost-Effective: Being open-source, Hadoop is a cost-efficient solution for managing large datasets.
- Distributed Processing: It uses a distributed file system to split data across multiple nodes for parallel processing.
What is Big Data?
Big Data refers to datasets so large and complex that traditional data processing tools can’t handle them efficiently. Big Data is often characterized by the 3 Vs:
- Volume: Massive amounts of data generated every second.
- Velocity: The speed at which data is generated and processed.
- Variety: Different types of data such as structured, semi-structured, and unstructured.
Hadoop is one of the key tools used to manage and analyze Big Data.
The Hadoop Ecosystem
Hadoop consists of various components that work together to provide a complete solution for storing and processing large datasets. Let’s take a closer look at the primary components.
1. Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
HDFS is the storage layer of Hadoop. It stores large files across multiple machines and ensures data replication for fault tolerance. HDFS follows a master-slave architecture where the master node (NameNode) manages the file system, and the slave nodes (DataNodes) store the actual data.
2. MapReduce
MapReduce is the processing engine of Hadoop. It divides a job into smaller tasks (Map) that can be processed in parallel across different nodes. After processing, it combines the results (Reduce) to produce a single output.
3. YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator)
YARN is responsible for managing resources in the Hadoop cluster. It allocates memory, CPU, and other resources to different applications running on the Hadoop system.
4. Hadoop Common
This includes common utilities and libraries needed by other Hadoop modules to function.
Additional Hadoop Ecosystem Tools
1. Hive
Hive is a data warehouse solution built on top of Hadoop. It allows users to query and manage large datasets using SQL-like syntax called HiveQL. It simplifies querying for those familiar with traditional databases.
2. Pig
Pig is a high-level data flow scripting language that simplifies the writing of complex MapReduce jobs. It’s ideal for ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes.
3. HBase
HBase is a NoSQL database that runs on top of HDFS. It allows real-time read and write access to large datasets and is well-suited for scenarios where low-latency data access is required.
4. Sqoop
Sqoop is used for transferring data between Hadoop and relational databases. It’s particularly useful for importing data into HDFS from MySQL, PostgreSQL, or other RDBMS systems.
5. Flume
Flume is a distributed service for collecting and moving large amounts of log data into HDFS in a scalable manner.
Use Cases of Hadoop
- Data Analytics: Hadoop is used to analyze large-scale datasets in industries like finance, healthcare, and retail.
- Log Processing: Organizations use Hadoop to store and analyze log files to identify trends and anomalies.
- Recommendation Systems: Companies like Netflix and Amazon leverage Hadoop to build recommendation engines based on user data.
- Social Media Analysis: Social platforms use Hadoop to process and analyze massive amounts of user-generated data.
Step-by-Step Guide to Hadoop Installation
You can set up a Hadoop cluster on your local machine or in the cloud. Here’s a quick guide to setting up Hadoop in a single-node configuration.
Prerequisites:
- Java: Hadoop requires Java to run.
- SSH: Secure Shell (SSH) for communication between nodes.
- Hadoop: Download Hadoop from the Apache Hadoop website.
Steps:
- Install Java:
sudo apt-get install openjdk-11-jdk - Download Hadoop:
wget https://apache.mirrors.lucidnetworks.net/hadoop/common/hadoop-3.3.6/hadoop-3.3.6.tar.gz - Extract and Configure Hadoop:
tar -xzvf hadoop-3.3.6.tar.gz cd hadoop-3.3.6 - Configure Environment Variables:
Edit
.bashrcto set Hadoop environment variables:export HADOOP_HOME=/path_to_hadoop export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/bin - Start HDFS:
Format the Namenode and start HDFS services:
hdfs namenode -format start-dfs.sh - Access Hadoop UI:
Open a web browser and navigate to
http://localhost:9870to access the Hadoop HDFS web UI.
Future of Hadoop and Big Data
With the rise of cloud computing, Hadoop’s role in Big Data continues to evolve. Cloud-native solutions such as Amazon EMR and Google Cloud Dataproc provide Hadoop services in the cloud, making it easier for organizations to deploy and manage Big Data infrastructure.
Resources:
Checkout by blogs

Leave a comment