How to Install IBM Watsonx Data 2.0 Developer Edition on Ubuntu EC2 (On-Premises)
Setting up IBM Watsonx Data 2.0 Developer Edition on an Ubuntu EC2 instance enables you to leverage IBM’s data lakehouse capabilities on the cloud. This guide provides detailed steps, from configuring entitlement to starting the Watsonx Data containers.
For guidance on creating an EC2 instance, check out my previous blog: How to Create an AWS EC2 Instance.Make sure the instance type bigger eg.t3.xlarge and allow All traffic
Prerequisites
Ensure that you have:
- An IBM Entitlement Key for Watsonx Data.
- An Ubuntu EC2 instance in AWS.
Step 1: Set Up Entitlement Key
- Log in to your IBM container library.
- Go to Add New key and create a new API key for entitlement.
- Store the API key securely, as you’ll need it for the Watsonx Data installation.
Step 2: Install Docker
Watsonx Data requires Docker to manage its containers. Install Docker as follows:
# Update package information
sudo apt update
# Install Docker
sudo apt install -y docker.io
# Start Docker service
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable docker
Verify Docker installation:
docker --version
Step 3: Set Up Installation Directory and Environment Variables
Switch to root user, create an installation directory, and set the necessary environment variables.
sudo su -
mkdir watsonxdata
cd watsonxdata
# Set environment variables
export LH_ROOT_DIR=<NEW DIRECTORY-watsonxdata>
export LH_RELEASE_TAG=latest
export IBM_LH_TOOLBOX=cp.icr.io/cpopen/watsonx-data/ibm-lakehouse-toolbox:$LH_RELEASE_TAG
export LH_REGISTRY=cp.icr.io/cp/watsonx-data
export PROD_USER=cp
export IBM_ENTITLEMENT_KEY=<YOUR_IBM_ENTITLEMENT_KEY>
export IBM_ICR_IO=cp.icr.io
Replace <YOUR_IBM_ENTITLEMENT_KEY> with the key obtained in Step 1.
For Docker, set DOCKER_EXE as follows:
export DOCKER_EXE=docker
Step 4: Download and Extract Watsonx Data Developer Package
-
Pull the Watsonx Data developer package and copy it to the host system:
$DOCKER_EXE pull $IBM_LH_TOOLBOX id=$($DOCKER_EXE create $IBM_LH_TOOLBOX) $DOCKER_EXE cp $id:/opt - > /tmp/pkg.tar $DOCKER_EXE rm $id -
Extract the package and verify the checksum:
tar -xf /tmp/pkg.tar -C /tmp cat /tmp/opt/bom.txt cksum /tmp/opt/*/* tar -xf /tmp/opt/dev/ibm-lh-dev-*.tgz -C $LH_ROOT_DIR
Step 5: Authenticate with IBM Registry
Log in to the IBM registry to authenticate and pull additional resources:
$DOCKER_EXE login ${IBM_ICR_IO} --username=${PROD_USER} --password=${IBM_ENTITLEMENT_KEY}
Step 6: Run Setup Script
Run the setup script to initialize the Watsonx Data Developer environment. You can set a custom password with the --password option; otherwise, the default password is password.
$LH_ROOT_DIR/ibm-lh-dev/bin/setup --license_acceptance=y --runtime=$DOCKER_EXE
Step 7: Start Watsonx Data Containers
Start the Watsonx Data containers using the following command:
$LH_ROOT_DIR/ibm-lh-dev/bin/start
Step 8: Access Watsonx Data Console
- Open the Watsonx Data console by visiting
https://<YOUR_EC2_PUBLIC_IP>:9443(or the port specified during setup). - Log in with the username
ibmlhadminand the password you set during setup (default ispassword).
Managing Watsonx Data
Check Container Status
To view the status of all containers:
$LH_ROOT_DIR/ibm-lh-dev/bin/status --all
Stop All Containers
To stop all containers:
$LH_ROOT_DIR/ibm-lh-dev/bin/stop
Start/Stop a Specific Container
To manage individual containers, use stop_service and start_service commands. Replace <container_name> with the name from the docker ps output:
$LH_ROOT_DIR/ibm-lh-dev/bin/stop_service <container_name>
$LH_ROOT_DIR/ibm-lh-dev/bin/start_service <container_name>
Step 9: Log In to Watsonx Data
Once Watsonx Data is up and running, access the login page via your browser at https://<YOUR_EC2_PUBLIC_IP>:9443.
Login Page: Enter your username and password to access the Watsonx Data console.
After that you will see the Dashboard
Step 10: Infrastructure Manager
After logging in, navigate to the Infrastructure Manager to monitor and manage system resources and services.
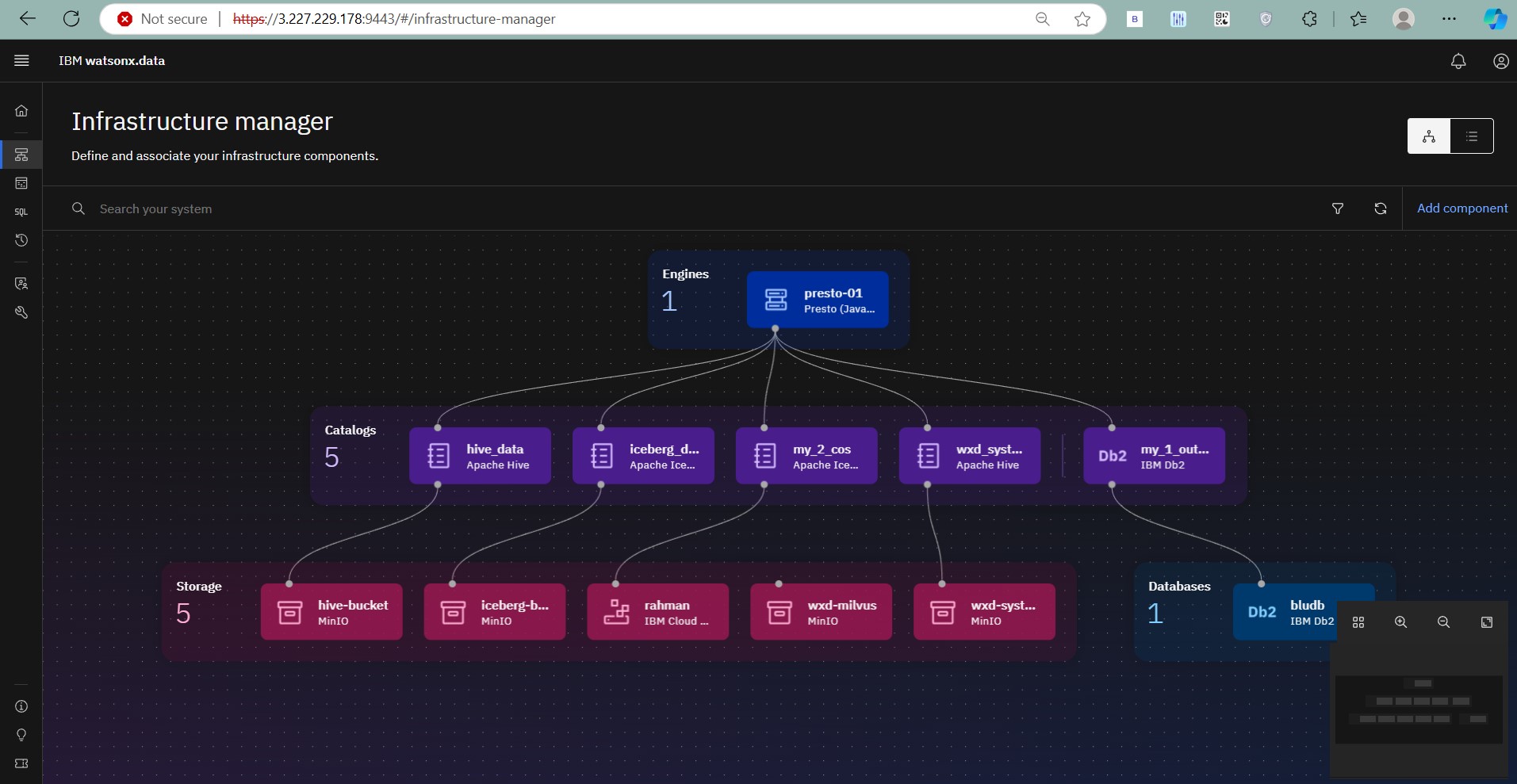
Infrastructure Manager: View and control Watsonx Data’s underlying infrastructure and resource allocations.
Step 11: Explore the Query Workspace
Use the Query Workspace to write and run SQL queries directly within Watsonx Data.
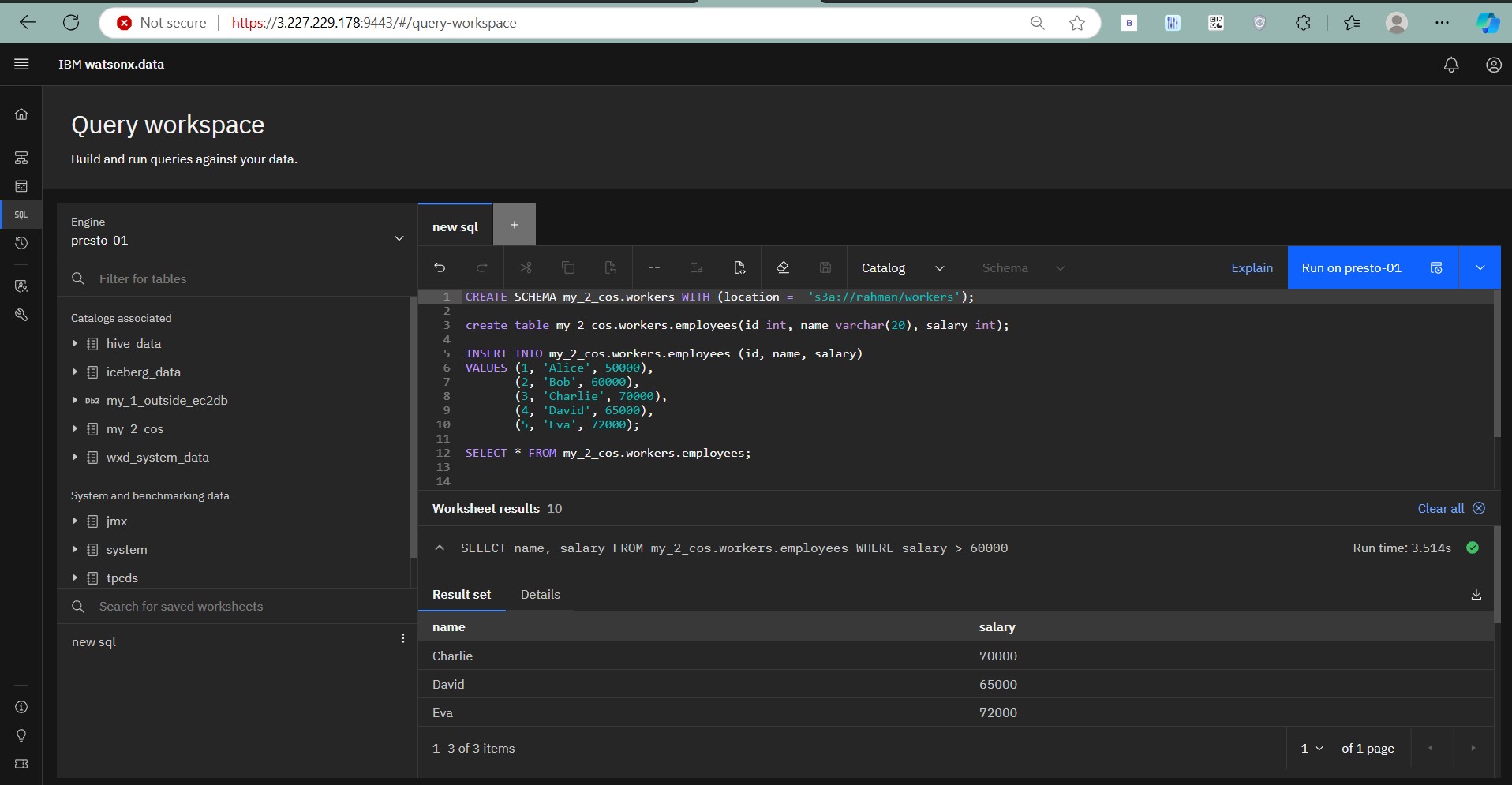
Query Workspace: Execute SQL queries and analyze data with Watsonx Data’s SQL editor.
Step 12: Access Query History
The Query History section lets you review past queries, making it easy to track, repeat, or debug previous SQL commands.
Query History: Review and manage past queries for efficient workflow management.
Congratulations! You have successfully installed and configured IBM Watsonx Data 2.0 Developer Edition on your Ubuntu EC2 instance.
Resources:
For more insights, check out my Blog Section.

Leave a comment