How to Set Up a Kubernetes Single Node Cluster Using Minikube on AWS EC2
Introduction
In this blog, I’ll guide you through the steps to Set Up a Kubernetes Single Node Cluster Using Minikube on AWS EC2. If you haven’t set up an EC2 instance yet, check out my previous Blog->Guide to creating an EC2 instance before proceeding.
Make sure Instance Size: t2.small (2 CPUs, 30 GB Storage). Note: This setup incurs costs as it’s beyond the free tier. Please shut down the instance when not in use to avoid charges.”
Prerequisites
- An active AWS account
- An EC2 instance (preferably Ubuntu)
- Basic knowledge of Linux command line
Kubernetes is a powerful tool for managing containerized applications at scale. But before diving into large-scale clusters, it’s helpful to practice on a smaller, local cluster. That’s where Minikube comes in!
In this blog, we’ll cover the basics of Minikube, kubectl, and how to manage pods and services (svc) on an EC2 instance. Let’s get started!
🌟 What is Minikube?
Minikube is a tool that allows you to run Kubernetes locally. It creates a single-node Kubernetes cluster that you can use to run Kubernetes commands, deploy apps, and experiment with configurations.
📦 What is kubectl?
kubectl is a command-line tool that lets you interact with Kubernetes clusters. You can use it to deploy and manage applications, as well as inspect and troubleshoot clusters.
🐳 What is a Pod?
A Pod is the smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes. It encapsulates containers (like Docker containers) that share the same network namespace and storage.
🔗 What is a Service (svc)?
A Service in Kubernetes exposes your application’s network on a cluster and connects Pods to the outside world (or to each other). The most common type of Service is NodePort, which opens a specific port on all cluster nodes for external traffic.
💻 Install kubectl on Ubuntu (x86-64)
- Log into your EC2 machine and Update packages:
sudo apt update - Download the latest kubectl release:
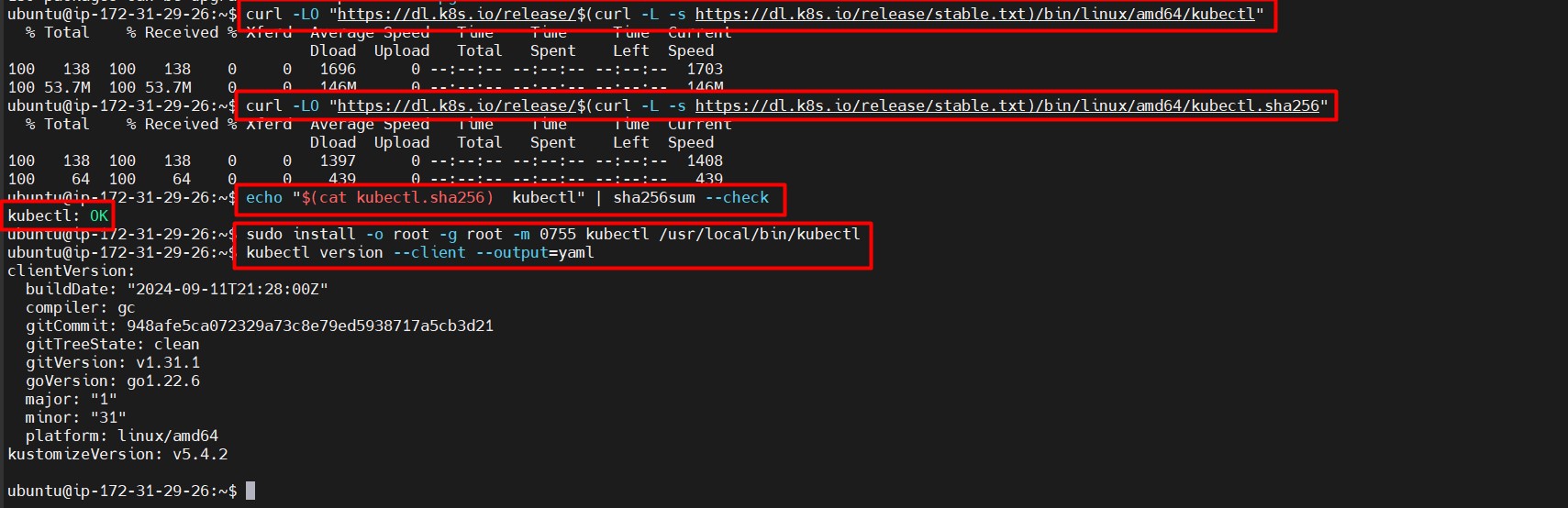
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl" - (Optional) Validate the binary:
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl.sha256" echo "$(cat kubectl.sha256) kubectl" | sha256sum --check # Output should be: kubectl: OK - Install kubectl:
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl - Check version for confirmation:
kubectl version --client --output=yamlReference image
🚀 Install Minikube
- Download Minikube for Linux:
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64 - Install Minikube:
sudo install minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube && rm minikube-linux-amd64Reference image
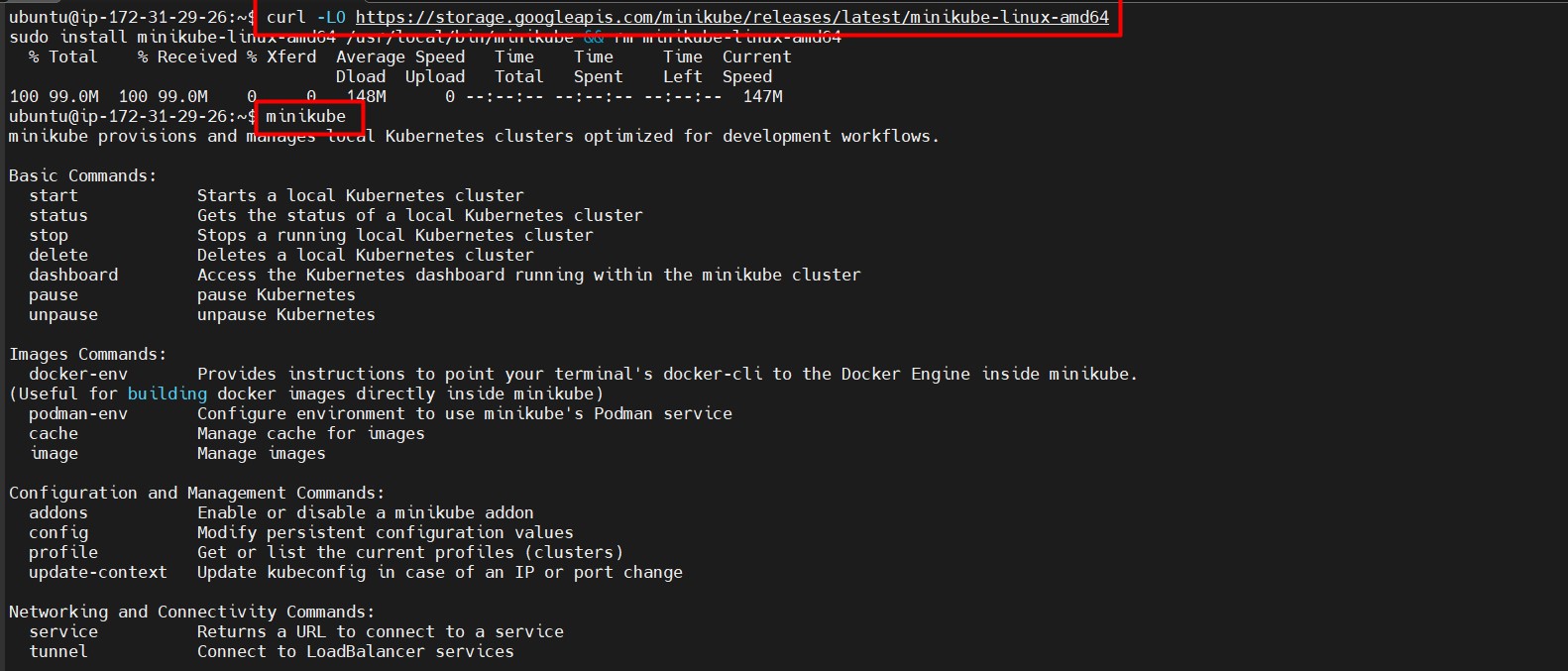
🛠 Setting up Minikube and Docker
Minikube requires a virtualization platform to create a virtual machine. We’ll use Docker as the virtualization driver.
- Install Docker:
sudo apt install docker.io -y - Check Docker version:
docker --versionReference image
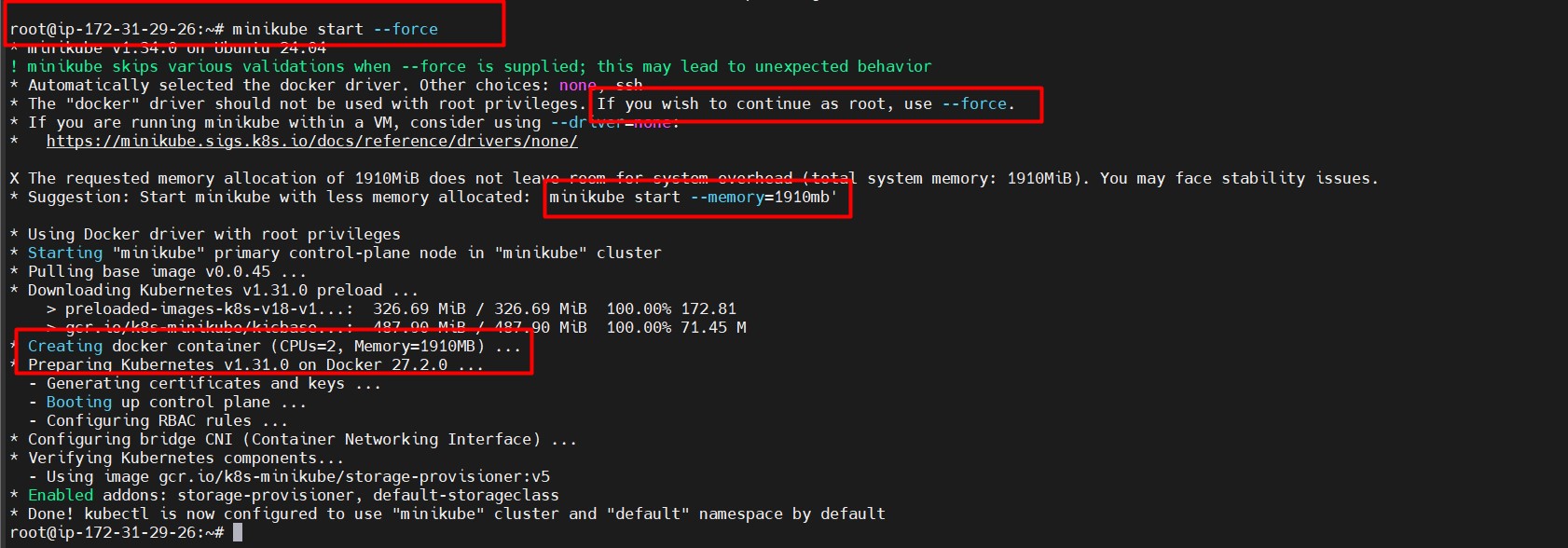
- Start Minikube as root user (important for running within EC2):
minikube start --force - Verify Kubernetes node status:
kubectl get nodesReference image
📄 Create and Manage Pods
- Define a simple NGINX Pod:
Create a file called
pods.ymlwith the following content:vi pods.ymlapiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: nginx:1.14.2 ports: - containerPort: 80Reference image u can get pods and nodes
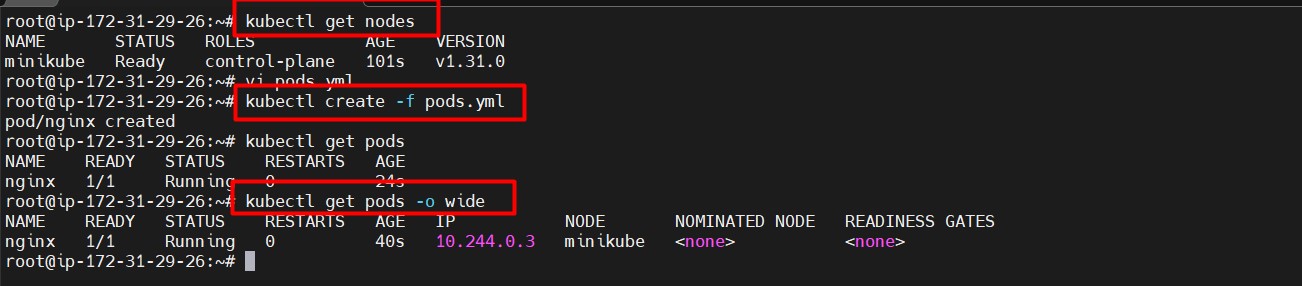
- Create the NGINX pod:
kubectl create -f pods.yml - List running Pods:
kubectl get pods - Get more details about the pod:
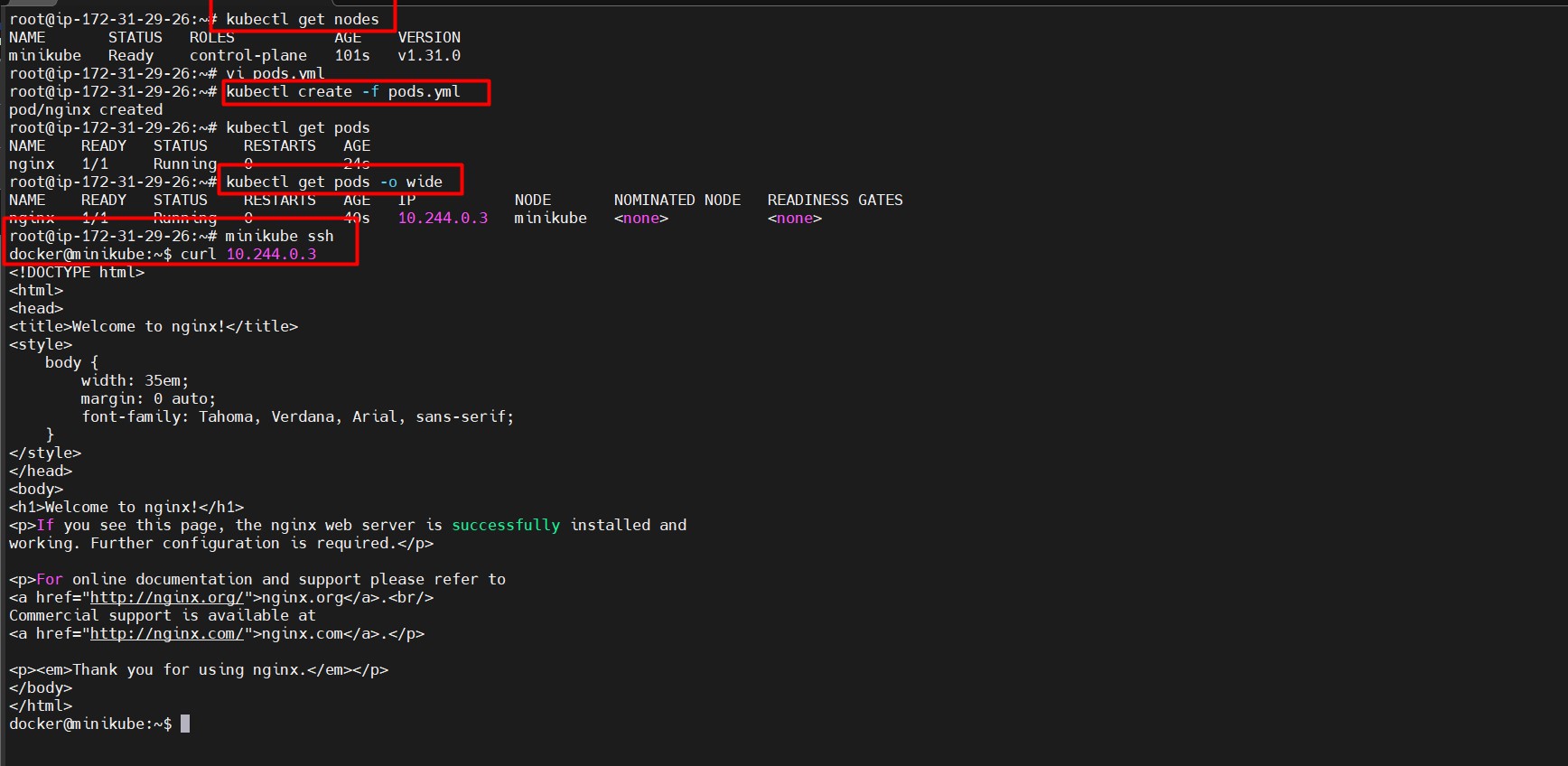
kubectl describe pod nginx - View logs of the NGINX pod:
kubectl logs nginxReference image U can access nginx pod in minikube ssh see below image
🔗 Expose Pod to Access from EC2 (NodePort)
- Label the pod for easier management:
kubectl label pod nginx app=nginx - Expose the NGINX pod using NodePort:
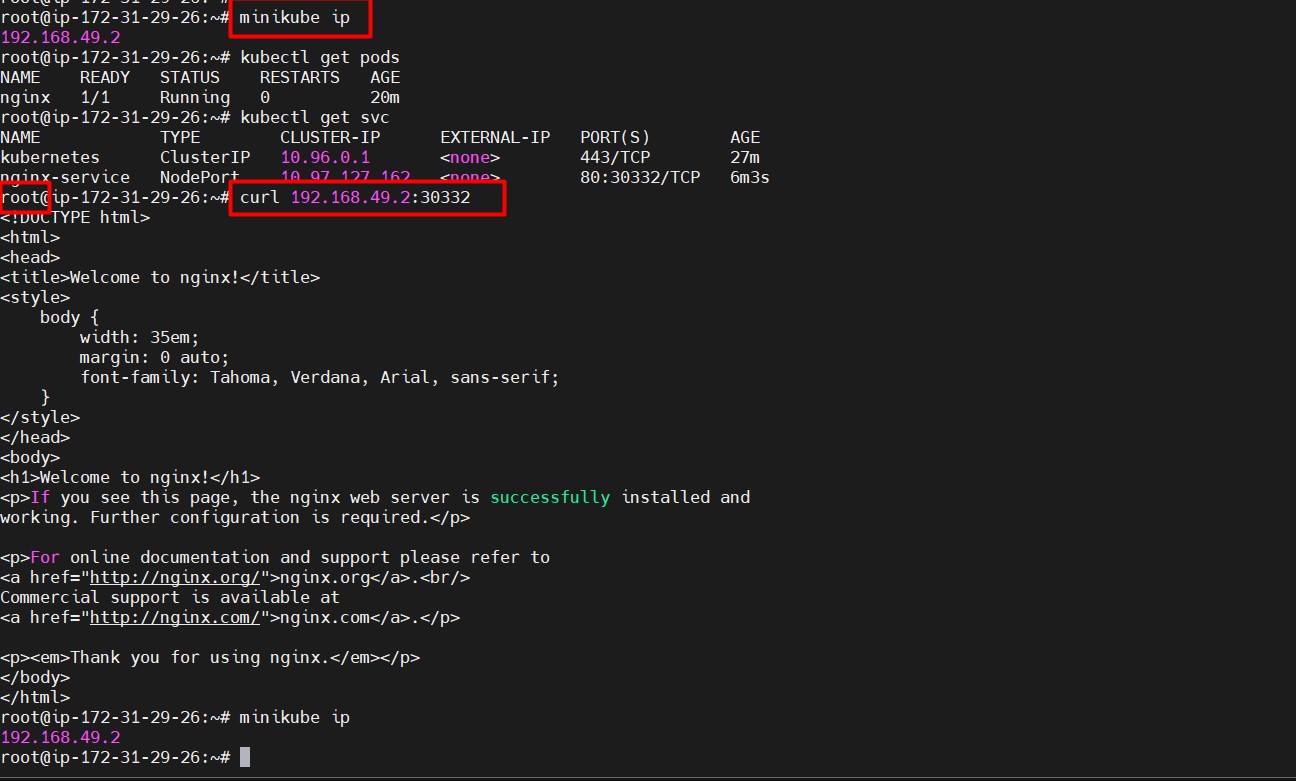
kubectl expose pod nginx --type=NodePort --port=80 - List services to find the exposed port:
kubectl get svc - Get the Minikube IP:
minikube ip - Test the service with curl:
curl http://<minikube-ip>:<node-port>Reference image U can access nginx pod in Ec2 level(node) see below image
🔍 Useful Commands for Managing Pods
- Delete a Pod:
kubectl delete pod nginx - List all Pods in wide view:
kubectl get pods -o wide - Apply configuration changes to a Pod:
kubectl apply -f pods.yml
By following these steps, you’ve successfully set up Minikube, deployed an NGINX pod, and exposed it externally on EC2 using NodePort. You can now explore more features of Kubernetes!

Leave a comment