What is Terraform: From Beginner to Advanced
Introduction
Terraform is a powerful Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool that allows you to define, deploy, and manage cloud resources in a repeatable and automated way. In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about Terraform, whether you’re just getting started or looking to advance your skills.
What is Terraform?
Terraform is an open-source IaC tool developed by HashiCorp. It uses a high-level configuration language known as HCL (HashiCorp Configuration Language) to define cloud infrastructure, making it cloud-agnostic and widely adopted for managing resources across AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and many other providers.
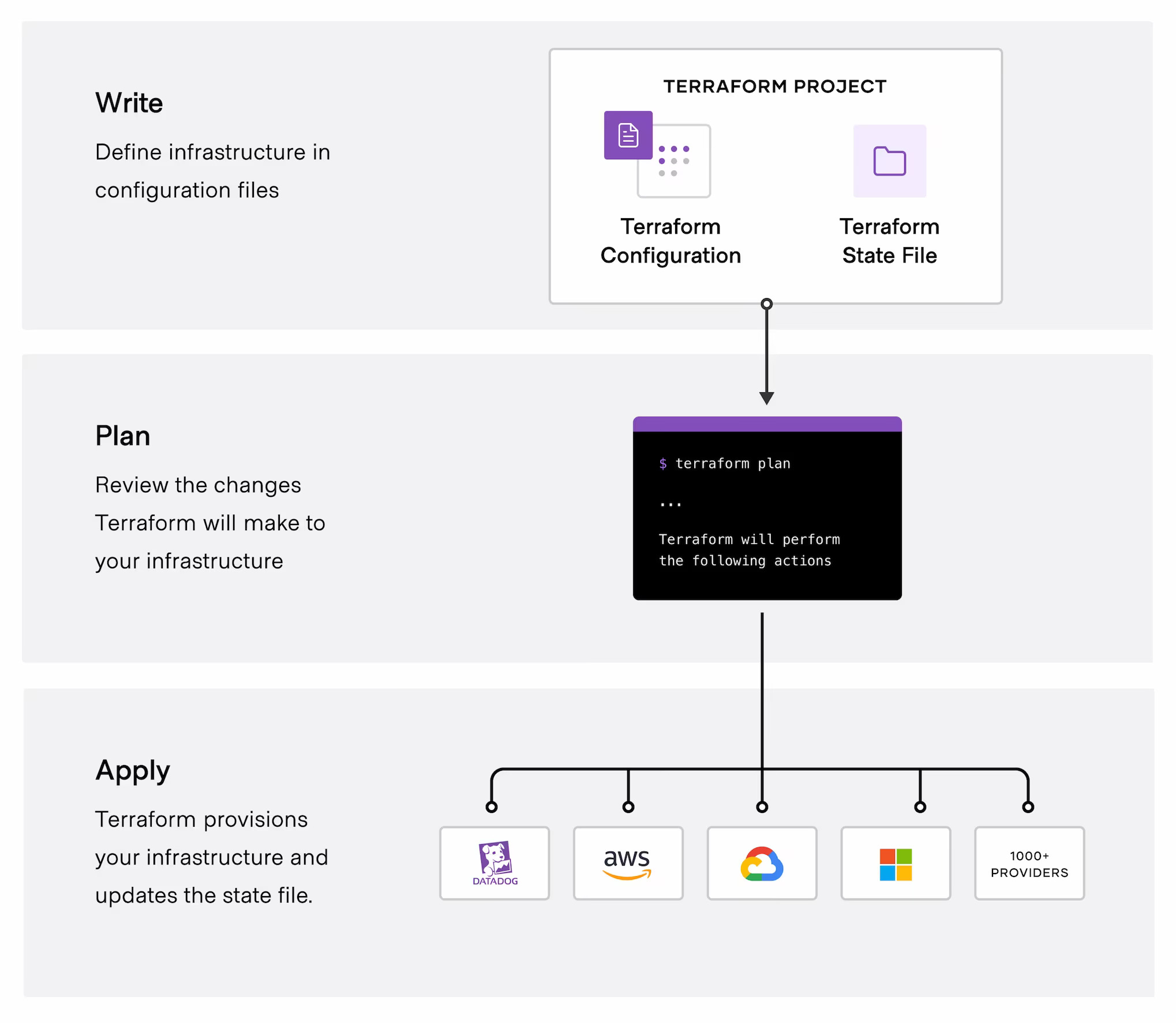
Why Use Terraform?
- Cloud Agnostic: Use a single configuration file for multiple providers.
- Version Control: Track changes in infrastructure like application code.
- Modularity: Reuse code with modules.
- State Management: Keep track of resource states, making updates and deletions easier.
Getting Started with Terraform
Follow these steps to install and configure Terraform:
Step 1: Install Terraform
Download the Terraform binary from Terraform’s official website and add it to your system’s PATH.
# On Ubuntu
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y terraform
# On macOS
brew install terraform
Step 2: Create Your First Configuration
Create a new file called main.tf and define a simple resource, such as an AWS EC2 instance:
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1"
}
resource "aws_instance" "example" {
ami = "ami-12345678"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
}
Step 3: Initialize and Apply
Run the following commands in your terminal to initialize and apply your configuration:
# Initialize Terraform
terraform init
# Apply Configuration
terraform apply
Step 4: Managing State
Terraform keeps track of your infrastructure’s state in a file called terraform.tfstate. Make sure to store this file securely, especially when working in teams.
Intermediate Terraform Concepts
Once you’re familiar with the basics, delve into these intermediate topics:
1. Variables and Outputs
Variables make your configuration flexible. Define variables in variables.tf:
variable "instance_type" {
default = "t2.micro"
}
Use outputs to extract information:
output "instance_id" {
value = aws_instance.example.id
}
2. Managing Multiple Environments
Use workspaces to manage different environments (e.g., dev, staging, production):
terraform workspace new dev
terraform workspace select dev
3. Modules
Modules allow you to reuse code and organize configurations. Create a module by defining resources in a separate directory, and reference it in your main configuration:
module "ec2_module" {
source = "./modules/ec2"
instance_id = var.instance_id
}
Advanced Terraform Techniques
For advanced users, consider these practices:
1. State Management and Locking
Use remote state backends (e.g., S3, Azure Blob Storage) and enable state locking to avoid conflicts:
terraform {
backend "s3" {
bucket = "my-terraform-state"
key = "state/terraform.tfstate"
region = "us-east-1"
}
}
2. Integrating with CI/CD
Use Terraform in a CI/CD pipeline to automate deployments. For example, with GitHub Actions:
# .github/workflows/terraform.yml
name: Terraform
on:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
terraform:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Setup Terraform
uses: hashicorp/setup-terraform@v1
- name: Terraform Init
run: terraform init
- name: Terraform Apply
run: terraform apply -auto-approve
3. Writing Custom Providers
Extend Terraform’s functionality by creating custom providers using Go.
Best Practices
- Use Version Control: Always version your
.tffiles. - Modularize: Break configurations into smaller, reusable modules.
- Implement State Locking: Use a remote backend with state locking.
- Automate with CI/CD: Integrate Terraform with your CI/CD pipelines.
Conclusion
Terraform is a versatile tool for managing infrastructure. Whether you’re a beginner looking to automate simple tasks or an advanced user managing complex cloud environments, mastering Terraform can significantly improve your DevOps skills.
For more resources:

Leave a comment